The Unified Access Multimedia Services application is used to configure the Multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) protocol. mDNS is used by "Zero Configuration Networking" solutions such as Apple's Bonjour, Avahi LGPL, and Linux NSS-mDNS. mDNS is a resolution service that is used to discover services on a LAN. mDNS allows the resolution of host names to IP addresses within small networks without the need of a conventional DNS server. The mDNS protocol uses IP multicast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets and is implemented by Apple Bonjour, Avahi (LGPL), and Linux NSS-mDNS. In a BYOD network, mDNS is leveraged by providing wireless guests and visitors access to network devices, such as printers. There are three types of mDNS that can be configured using OmniVista.

Gateway mDNS is used if the network has no WLAN controller. In this mode, the traffic from the edge switch is forwarded to the configured gateway switch. The OmniSwitch acts as a gateway to flood mDNS messages over designated switch VLANs. A Gateway mDNS Switch replaces the Wireless Controller used in Legacy mDNS, and can be used if there are Stellar APs in the network. Wireless clients connected to APs request the mDNS service offered. The mDNS message from the Bonjour capable wired service device is encapsulated and relayed to the Gateway OmniSwitch. The Gateway OmniSwitch then relays the mDNS messages received to the APs over the designated Gateway VLANs. All of the devices with which you want to communicate must be connected to the VLANs specified when the Gateway Switch is configured.
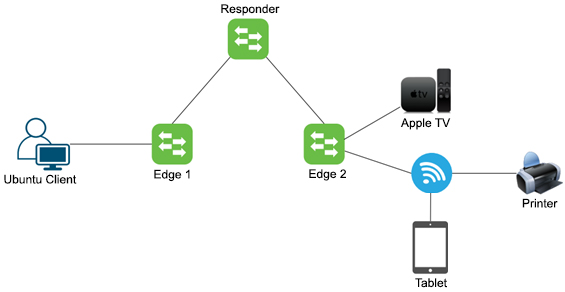
Responder mDNSis configured on Responder Switches which communicate with Edge Switches/Stellar APs to which clients connect. In this mode, the Responder Device acts as a core switch. Server Rules are created on the Responder Device that contain Sever Policies and Client Policies. The Service Rules define the criteria by which the Responder Device decides which services can be shared with which client requests.
Notes:
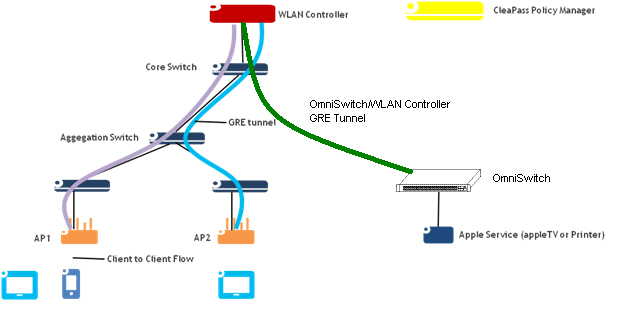
Legacy mDNS is configured on an OmniSwitch by creating a GRE Tunnel between the OmniSwitch and a Wireless LAN Controller. The following figure below provides a sample mDNS workflow setup. The wireless clients connected to Access Point 1 (AP1) or Access Point 2 (AP2) request the mDNS service offered.
The mDNS feature is enabled on the OmniSwitch to support the mDNS service. A Layer 2 GRE tunnel interface is configured from the WLAN controller to the OmniSwitch to relay the mDNS messages. The mDNS message from the Bonjour capable wired service device is encapsulated and relayed from the OmniSwitch to the configured WLAN controller over the GRE tunnel. The WLAN controller then relays the mDNS messages received via the OmniSwitch GRE tunnel to the APs over the AP GRE tunnels.
Note that the WLAN controller uses a multicast optimization algorithm and forwards Bonjour response messages to targeted user devices, instead of all devices on all APs. This limits the unnecessary flooding of the Bonjour/mDNS traffic to improve the Wi-Fi performance.